Authors: Prof. Augusto Bessa and Prof. Íris Sol
Initial evaluation
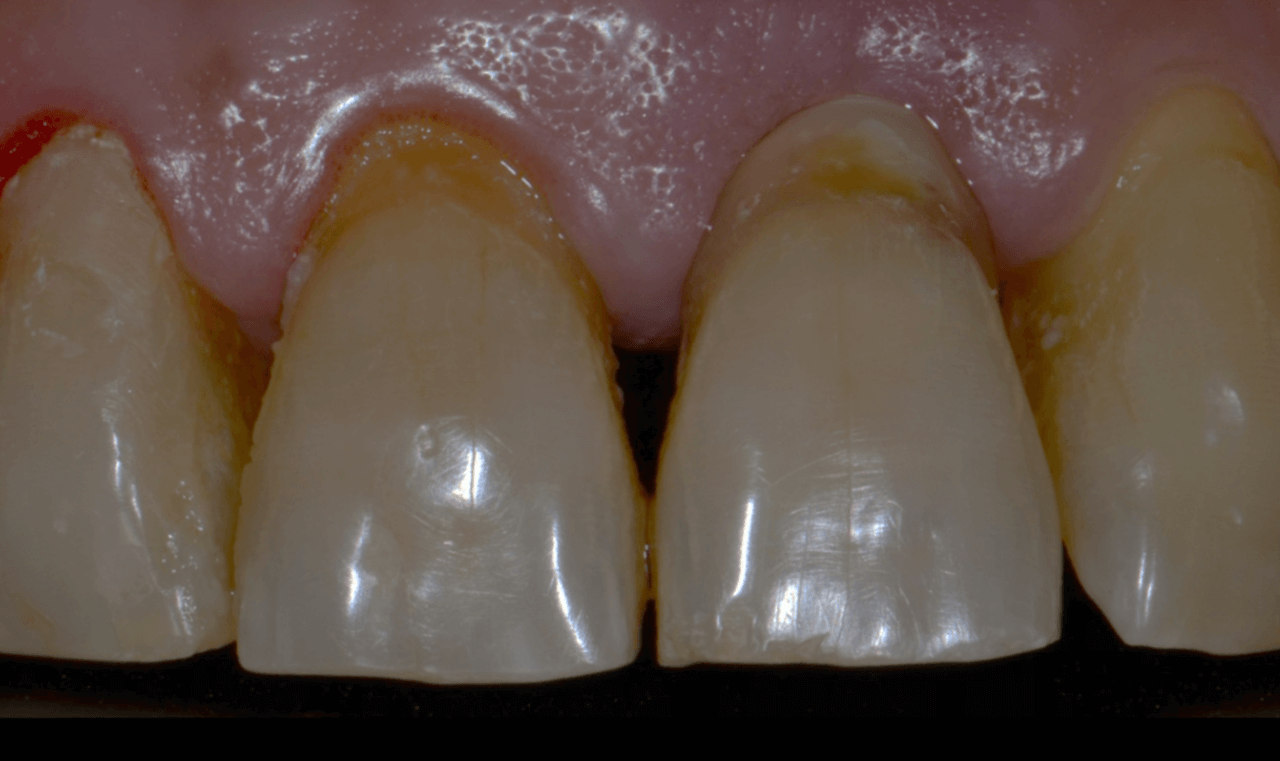
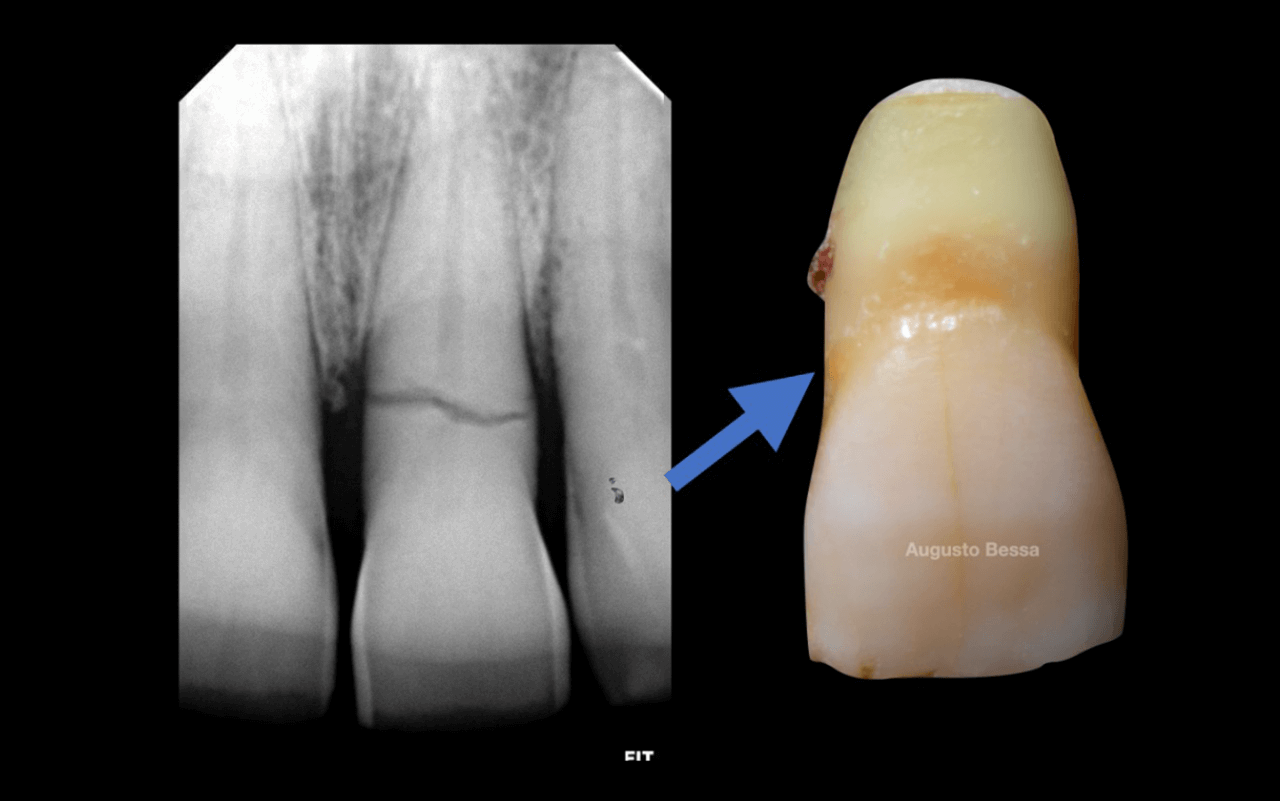
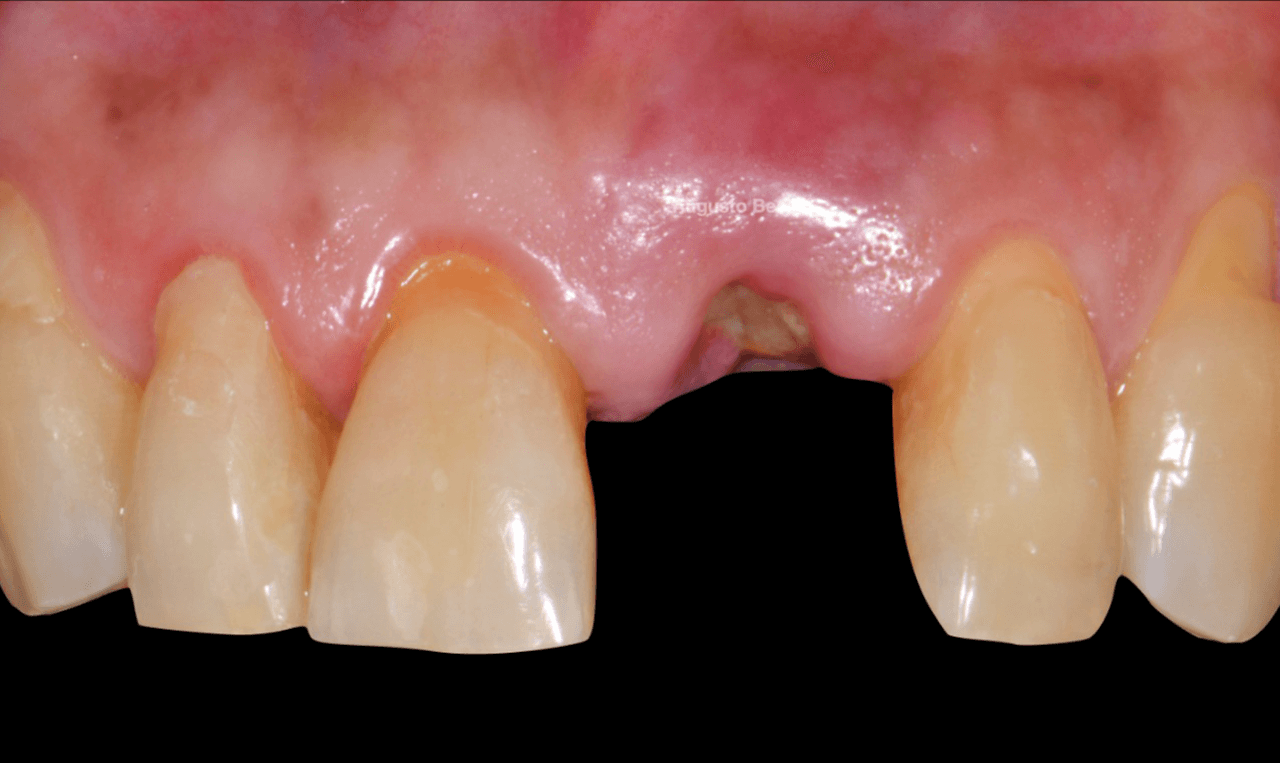
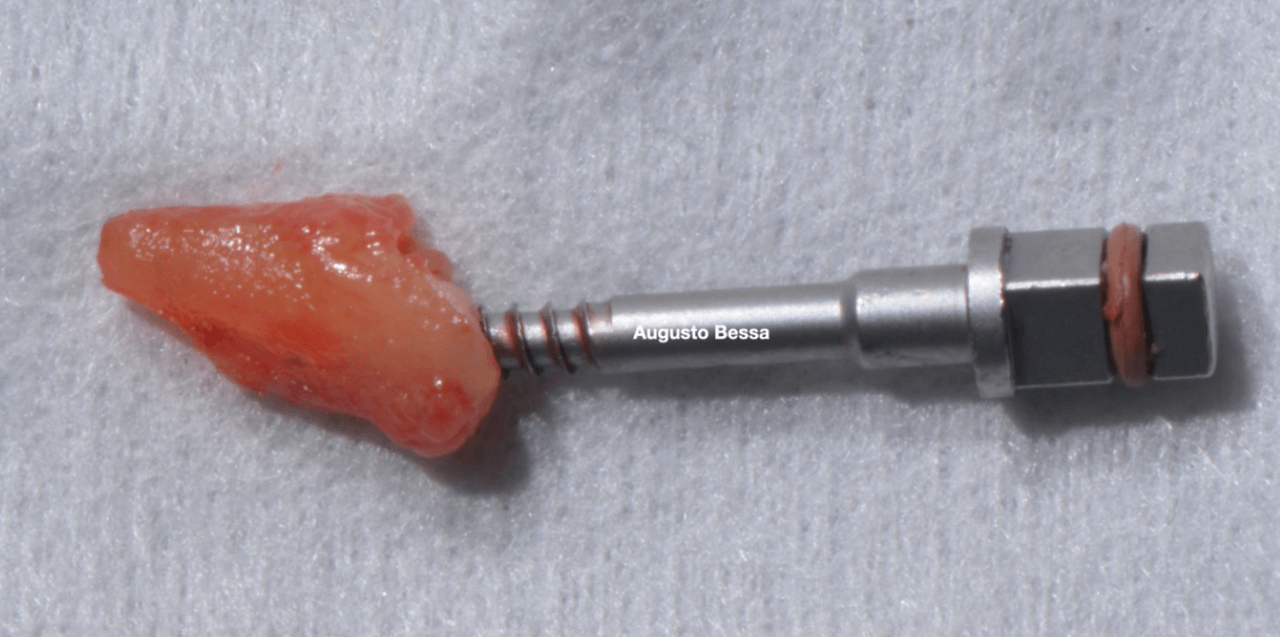
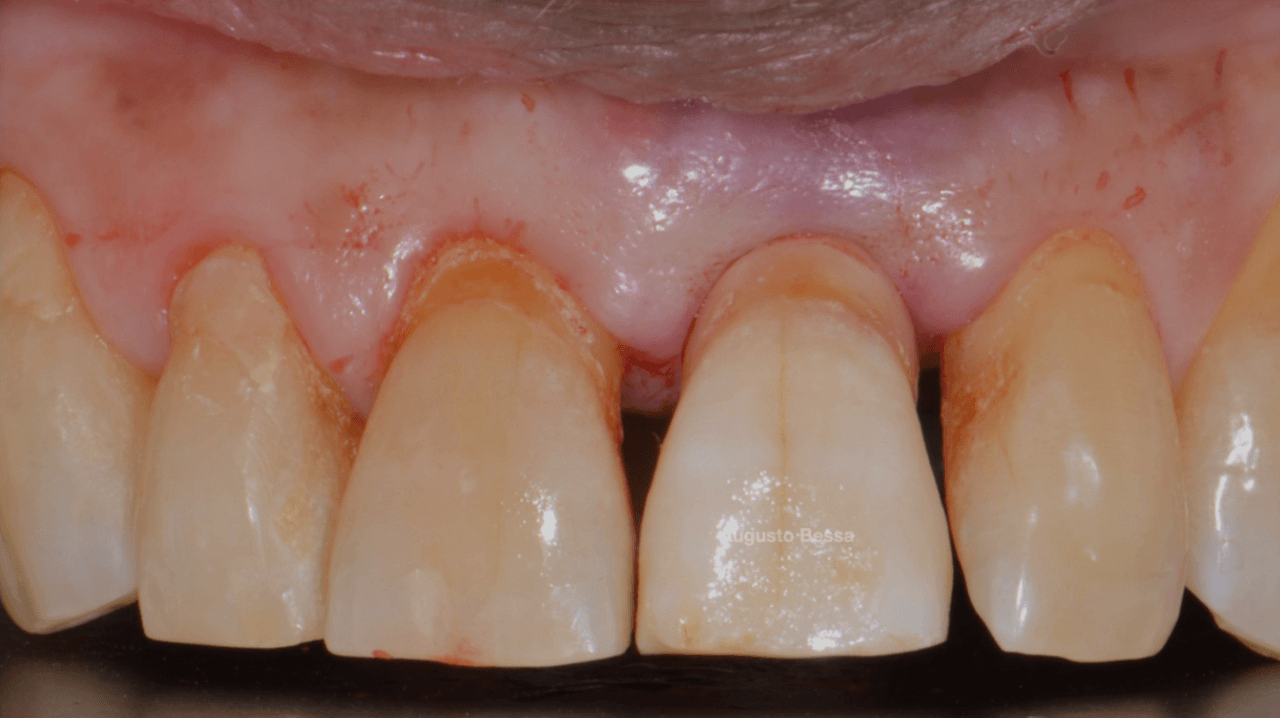
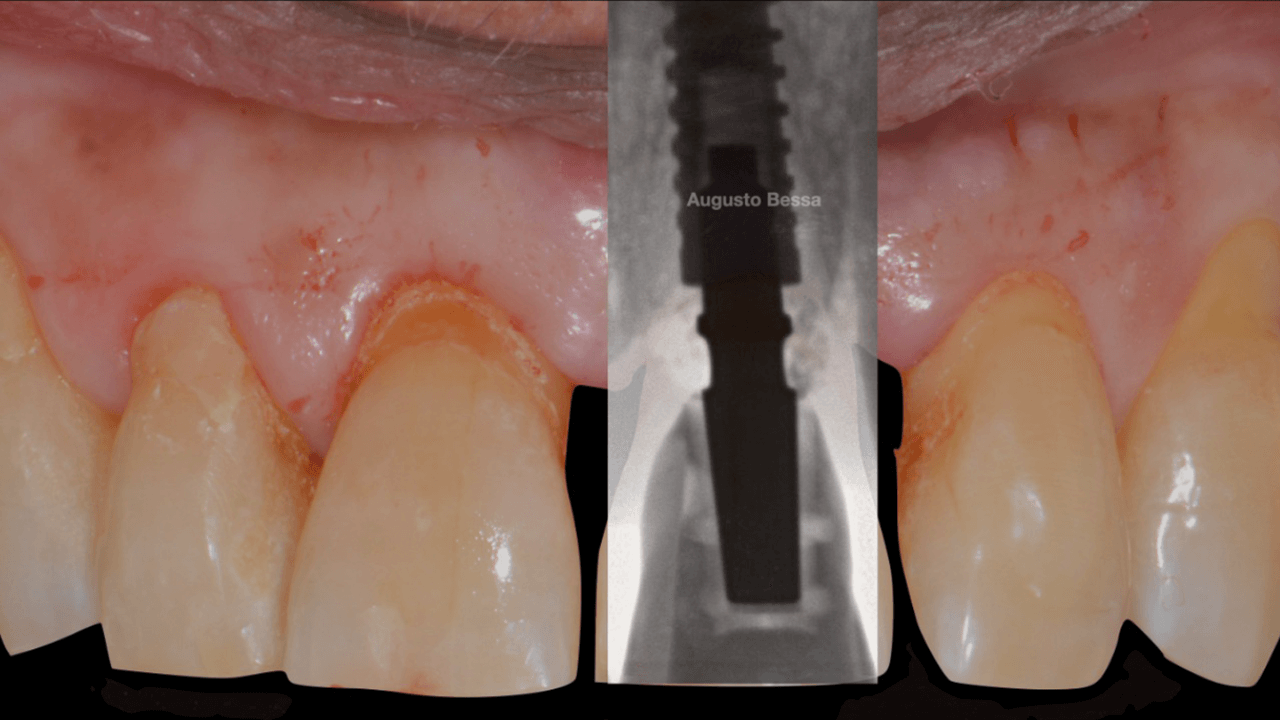
Male patient, 61 years old, went to the private dental clinic after suffering trauma to dental element 21 (Fig. 1). The clinical examination showed mobility of the crown, and the horizontal fracture was confirmed by the periapical radiographic examination (Figs. 2 and 3), and surgical removal of the root and rehabilitation with an implant was indicated. After the tomographic examination, the case was built virtually in the 3Shape Implant Studio program, and the planning for the atraumatic exodontia of the root remains was carried out (Fig. 4), aiming to preserve the sorrounding bone structure and facilitate the surgery for installing the immediate implant. The chosen implant system was Arcsys by FGM.
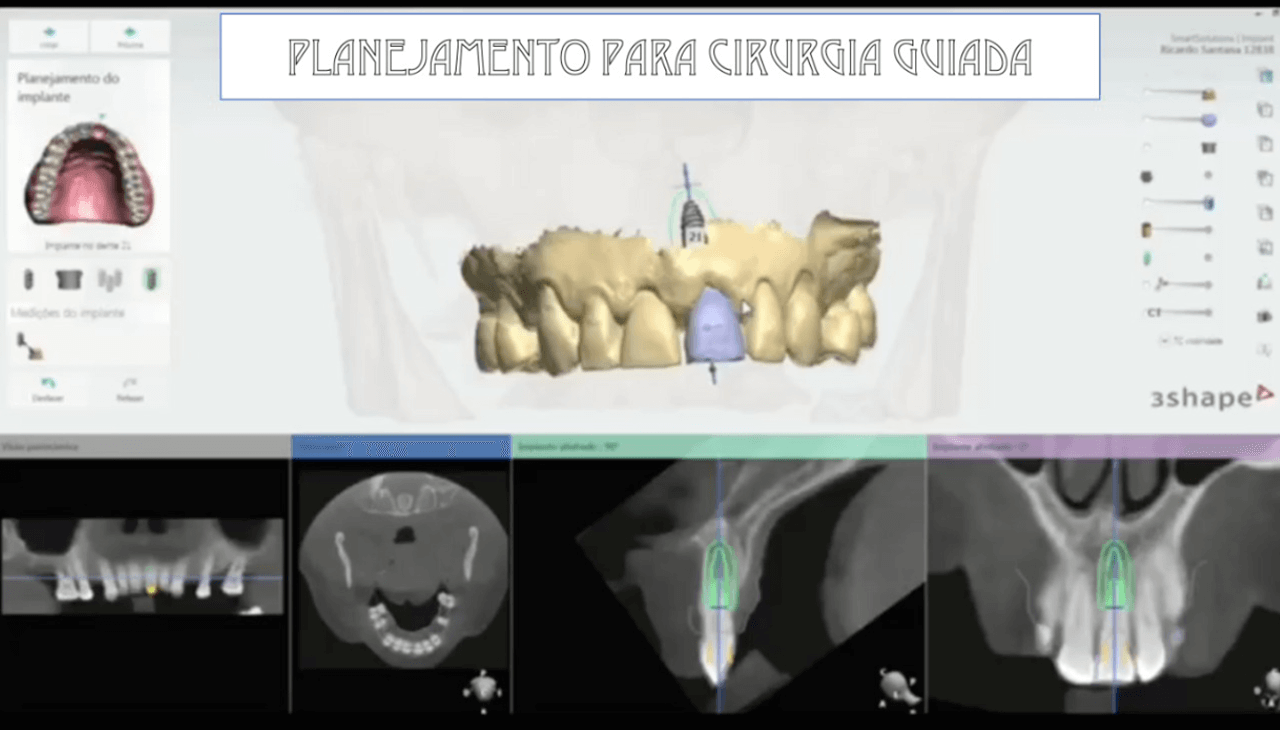
Before the surgery, the virtual surgical guide was planned, joining the STL file of the scanning to the DICOM file of the tomography in a specific planning software (Figs. 5 and 6).
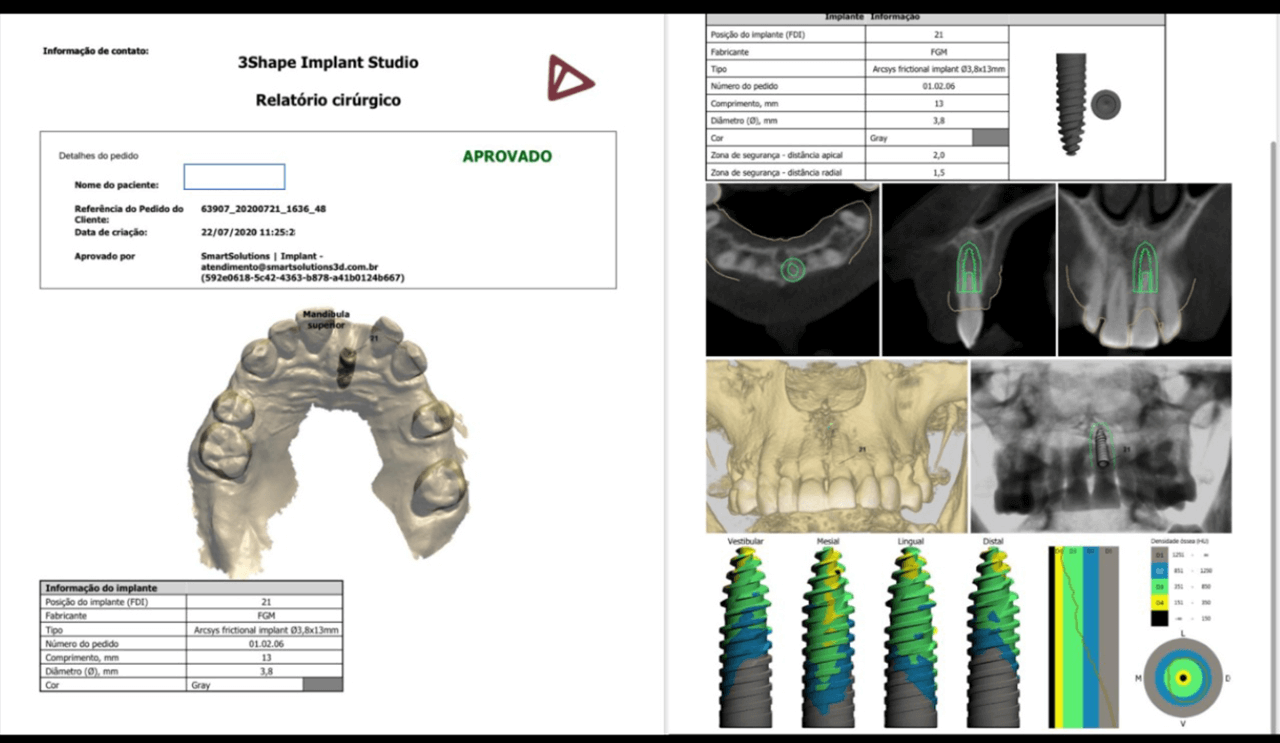
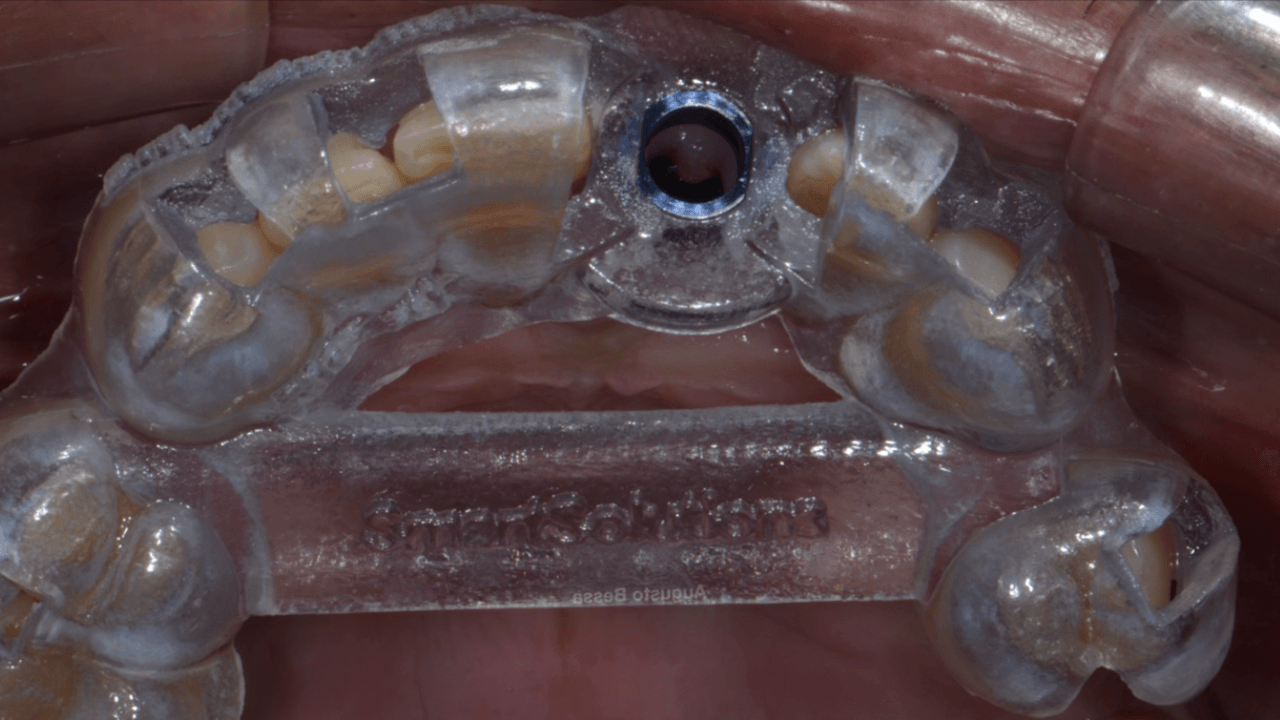
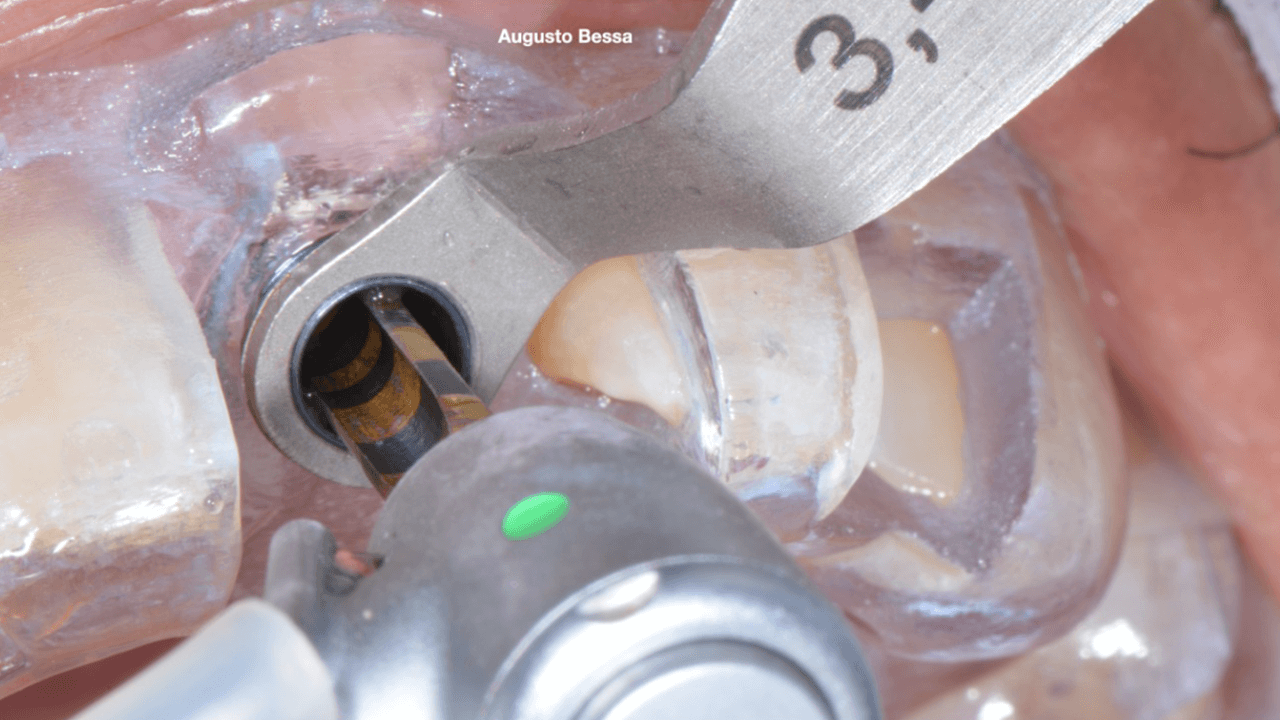
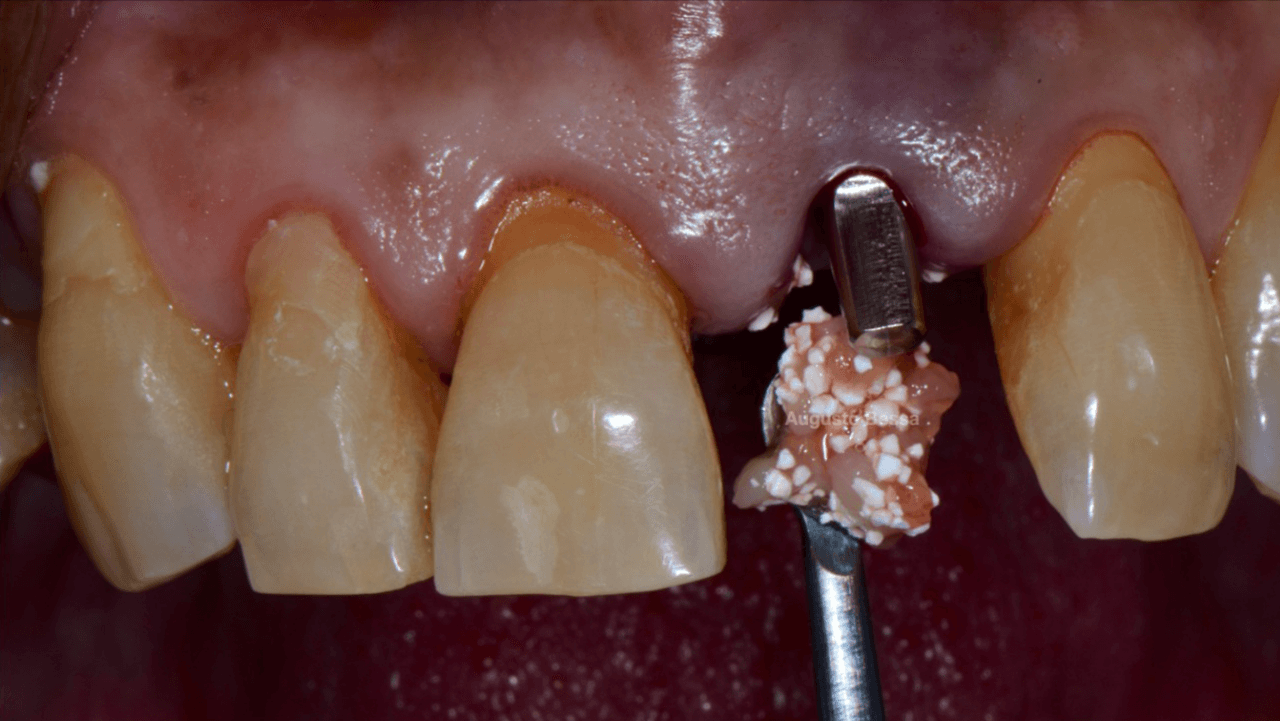
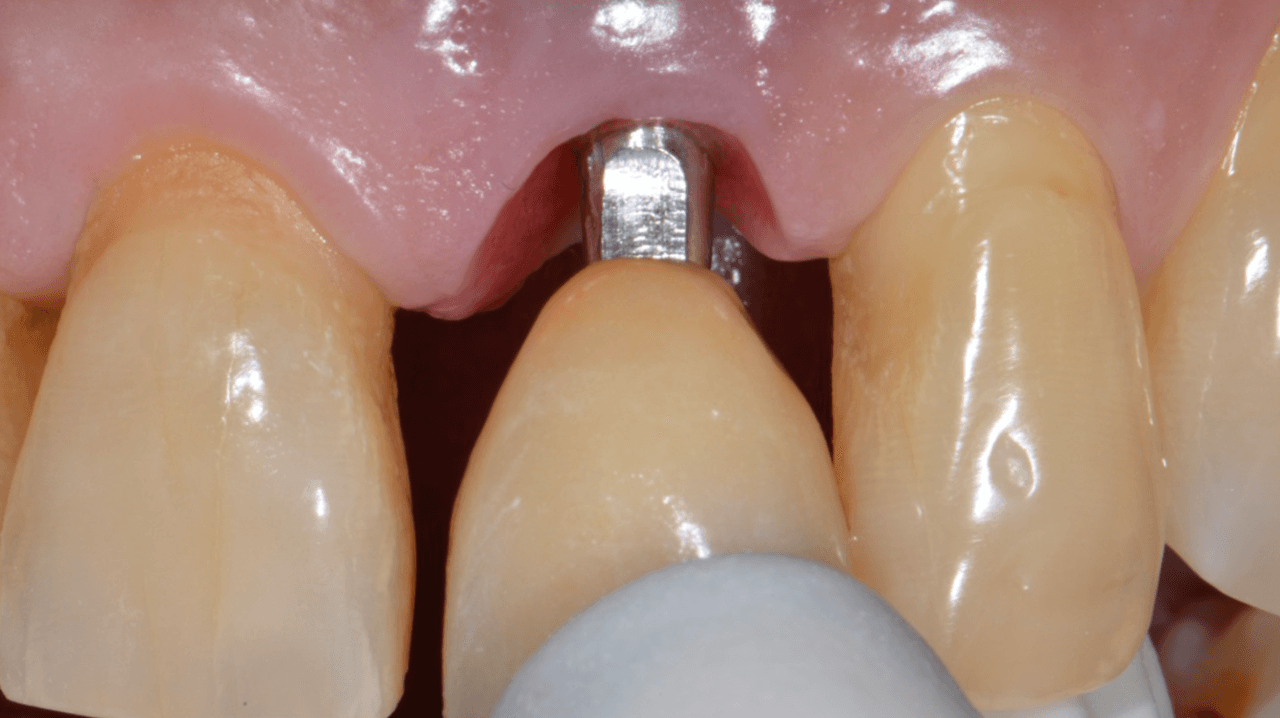
With the aid of the surgical guide printed from the virtual planning (Fig. 7), the surgical instrumentation was executed to install a 3.8 mm x 13 mm implant (Fig. 8). The implant was installed (Fig. 9) and anchored to the alveolus. A 3 mm x 6 mm Arcsys prosthetic abutment with a 4.5 mm transmucosal portion was activated according to the protocol recommended by the manufacturer. The filling with the Nanosynt bone graft with granulation from 500 µm to 1000 µm was performed (Fig. 10), associated with the chopped L-PRF fibrin.
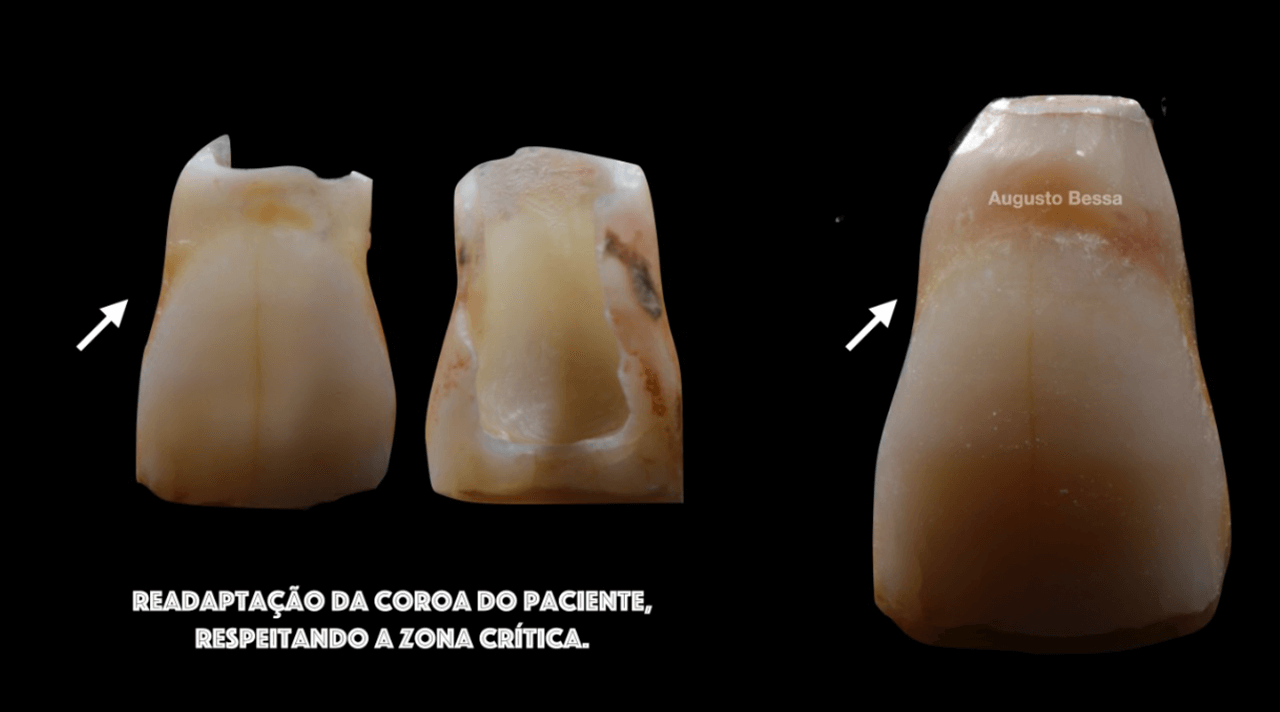
A provisional crown was made immediately through the fractured crown, respecting the critical zone (Fig. 11). After polishing and finishing, it was cemented to the abutment with provisional cement (Figs. 12 and 13).
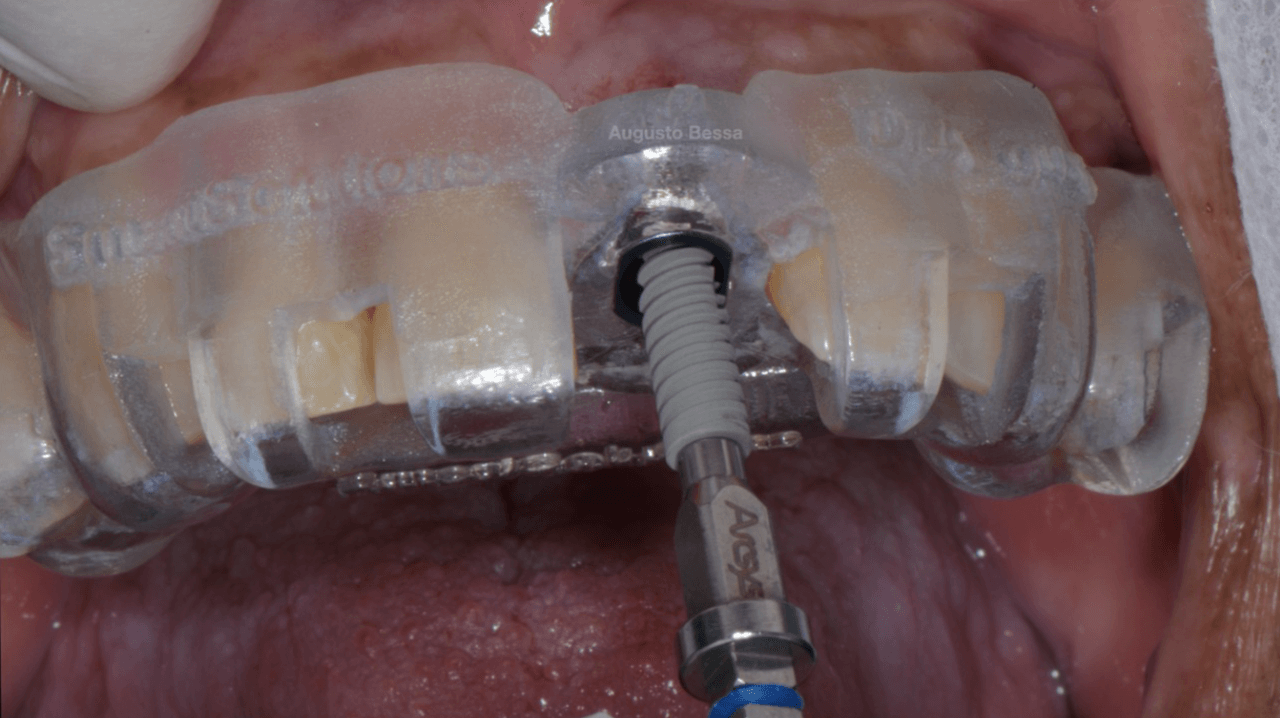
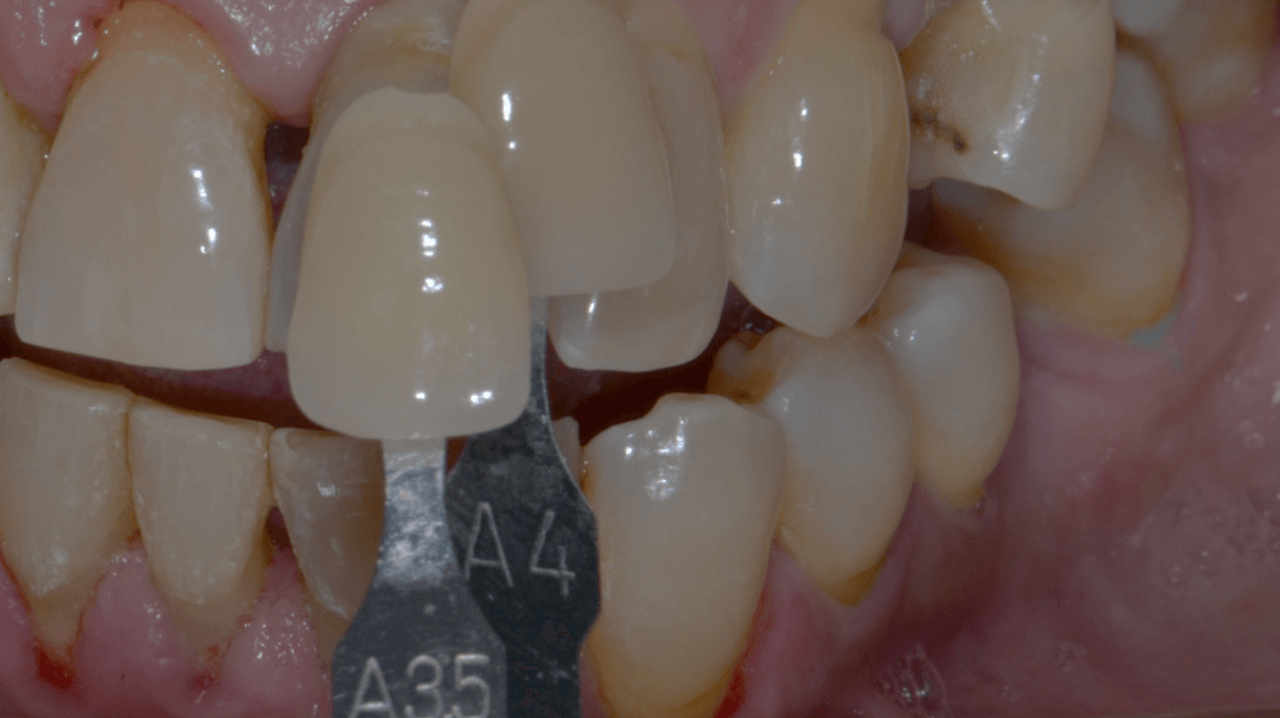
After 4 months of waiting for the bone remodeling of the alveolus and the osseointegration of the implant, we proceeded to execute the connective tissue graft, improving the pink peri-implant esthetics. After this step healed (Fig. 14), the prosthetic rehabilitation was planned, also in the digital workflow. For such, the Scan Body for abutments was used, designed with an inspection window to facilitate its visualization on the prosthetic component (Figs. 15 and 16). The selection and photography of the colors were performed to send to the laboratory (Fig. 17).
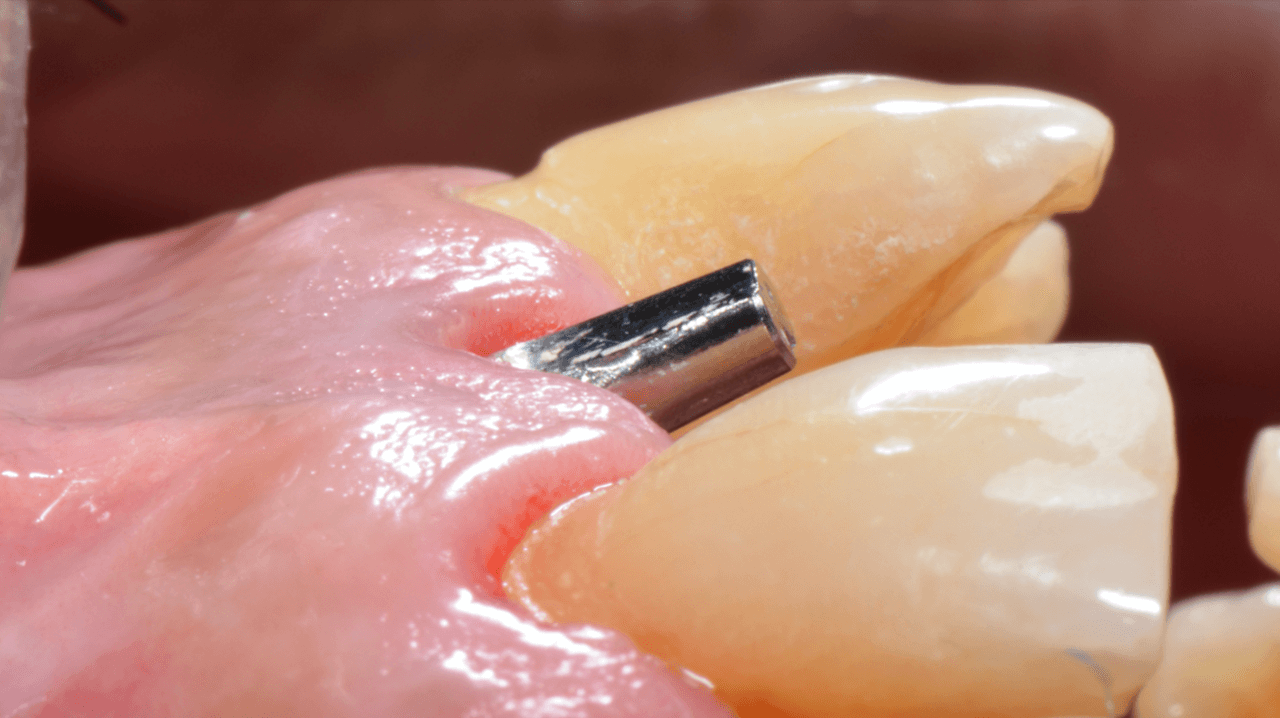
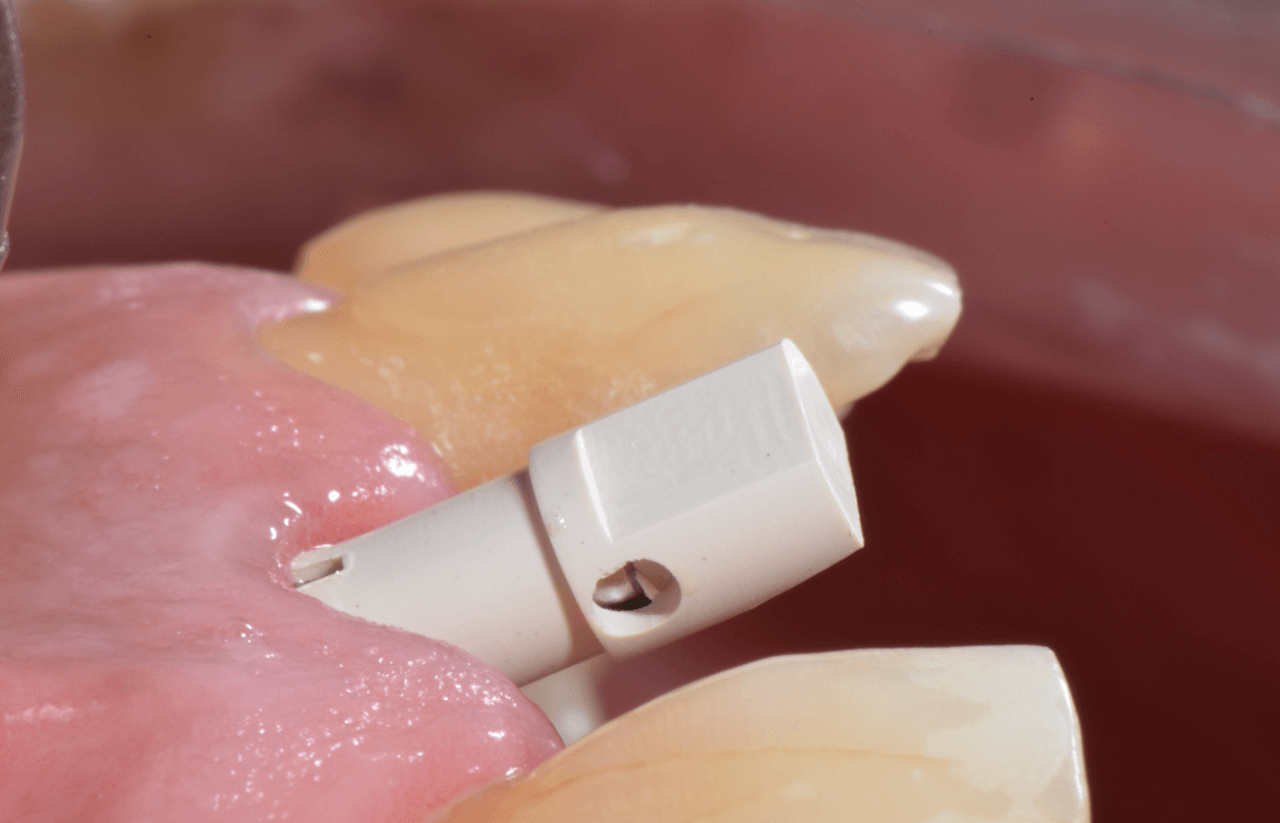
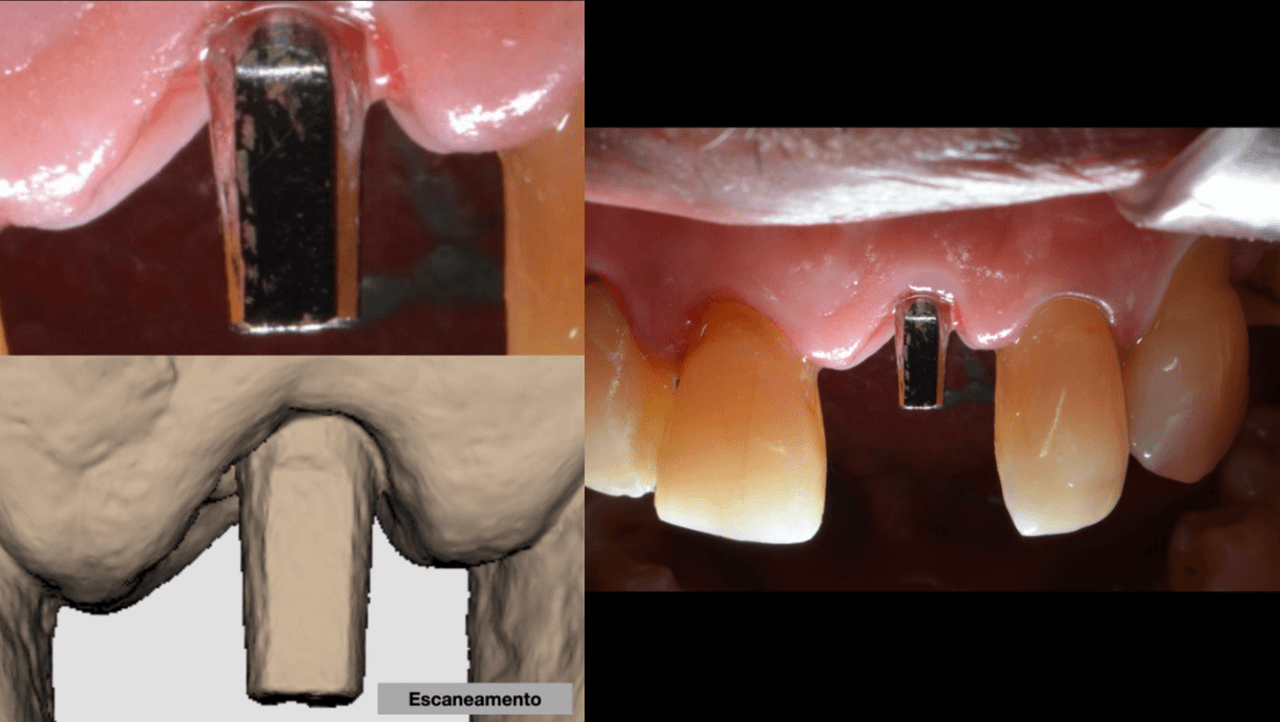
Considering that the library of Arcsys implants and components is available in the 3Shape software, the CAD operator planned, designed, and milled a zirconia cast and performed the stratification of the ceramics. Upon removing the provisional crown, the healed emergence profile with the tissue positioned favorably was observed (Fig. 18).
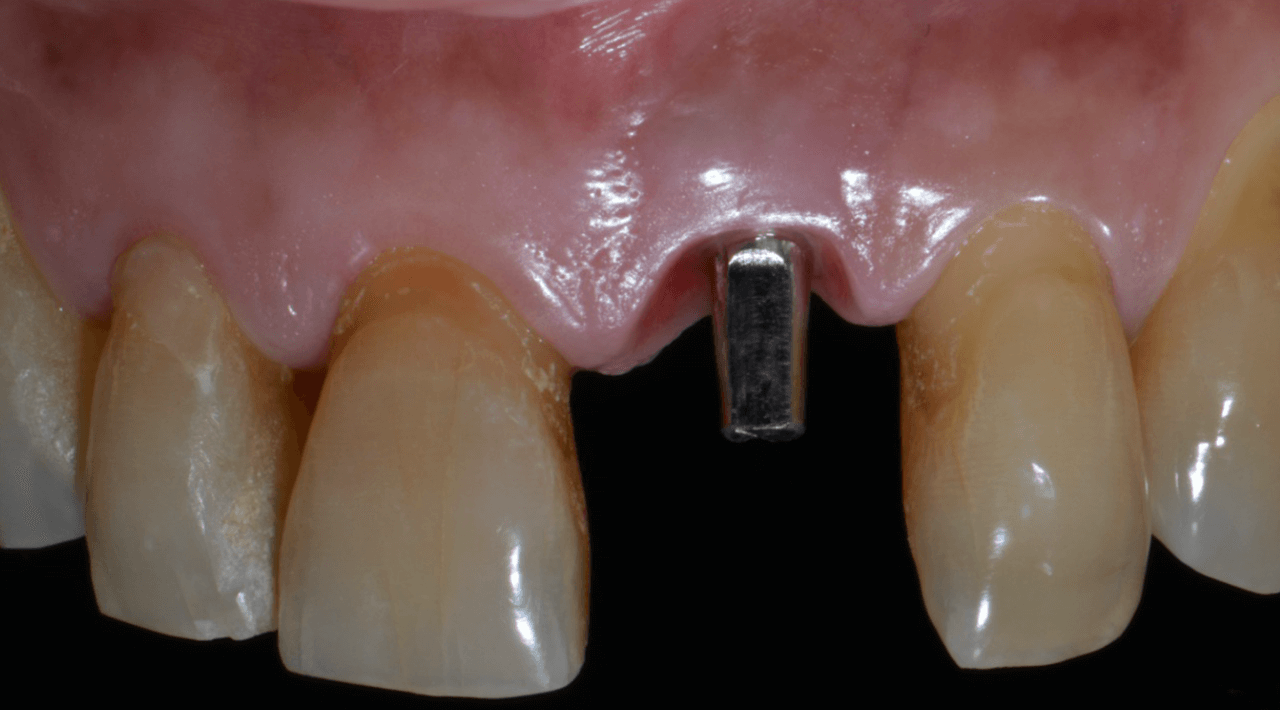
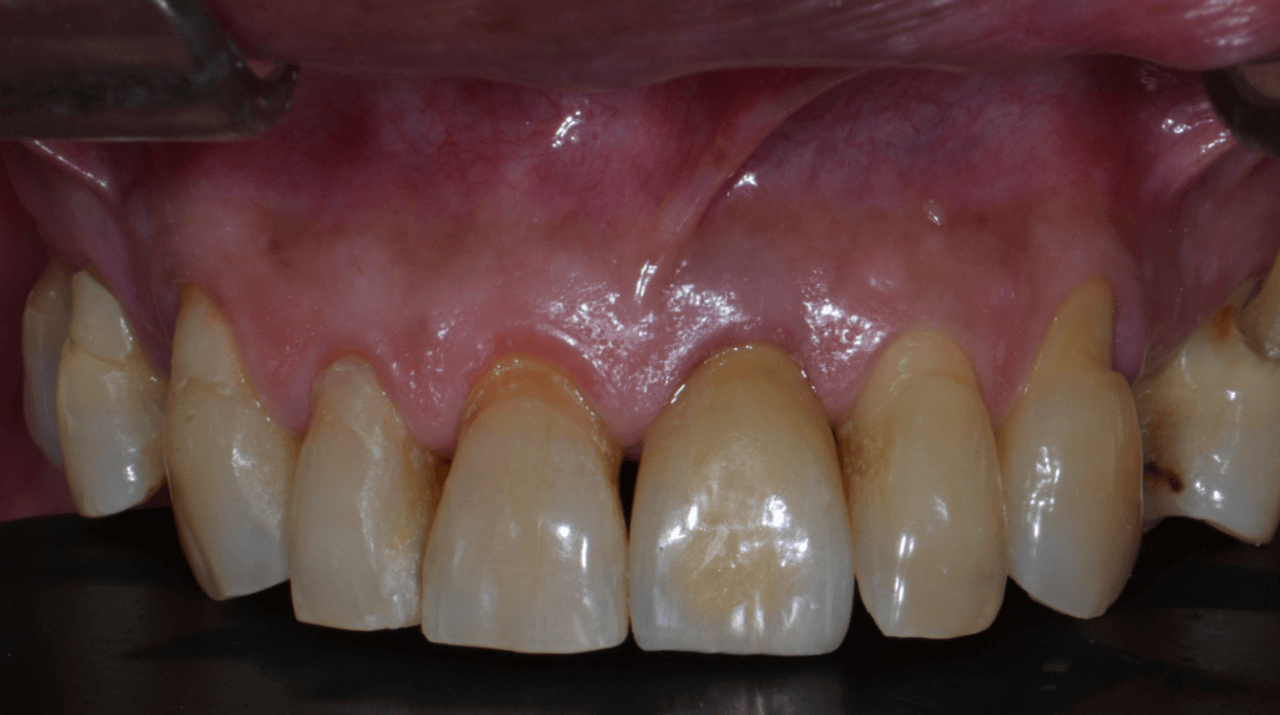
The case was finalized with a perfect adaptation (Fig. 19), and the definitive prosthetic cementation was performed (Fig. 20). The replacement of dental elements in the anterior region using the digital flow results in more significant swiftness in the surgical act and facilitates the clinic’s day-to-day, increasing the comfort, precision, and quality of the results.
References
- Catálogo de produtos da FGM Dental Group;
- Regeneração Óssea Guiada na Implantodontia
Daniel Buser – Quintessence Editora – 2010 - Regeneração Guiada Tecidual
Mauro Cruz – Editora Santos – 2006 - Enxertos ósseos em Implantodontia
Jean-François Tulasne e Andreáni – Quintessence Editora – 2010 - Enxertos Ósseos em Implantodontia
Reanato Mazzonetto et al. – Napoleão Editora – 2012 - Transplantes Ósseos na Implantodontia
André Antonio Pelegrine et al. – Napoleão Editora – 2008 - Catálogo de produtos da FGM http://www.fgm.ind.br/site/produtos/implantesbiomateriais/substituicao-ossea-nanosynt/
- Choukroun, J. (2001) Une opportunit_e en paroimplantologie: le PRF. Implantodontie, 42, 55– 62. French.
- Pan J, Xu Q, Hou J, Wu Y, Liu Y, Li R, Pan Y, Zhang D. Effect of platelet-rich fibrin on alveolar ridge preservation: A systematic review. J Am Dent Assoc 2019; 150:766-78. doi: 10.1016/j.adaj.2019.04.025.

![Tratamento de fratura em incisivo central superior com 11 - Treatment of a fracture on an upper central incisor with rehabilitation through immediate implant carried out with a virtual surgical guide: a clinical case report Tratamento-de-fratura-em-incisivo-central-superior-com-1[1]](https://srv01.fgmdentalgroup.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/11/Tratamento-de-fratura-em-incisivo-central-superior-com-11.jpg)