Prof. Dr. Diego Bazan
Prof. Dr. Fabio Lorenzoni
Male patient, 51 years old.
Chief complaint: Dental fracture.
Initial evaluation: Patient fractured element 26 where there was an amalgam restoration that involved a large part of the mesiopalatine cusp. The fracture extended far beyond the cement-enamel junction, close to the marginal bone crest and compromised the biological space.
Treatment performed
As it was not possible to perform surgery to recover the biological distance and promote periodontal health, and in order to preserve the interradicular septum so that the installation of an implant was possible in the same surgery, a minimally traumatic extraction was performed with dental sectioning. After extraction and bone preservation, a 4.3x5mm Arcsys® implant (FGM) was installed at the site with a torque of 10N. The root alveoli were filled with Nanosynt® sticky bone (FGM). To close the socket of the alveolus, 4 autologous leukoplate fibrin or LPRF membranes and the open wound technique were used, aiming to form a greater amount of keratinized soft tissue on the site. The patient was evaluated after 7 and 30 days.
After 4 months of healing, reopening surgery was performed. Excellent local bone formation was observed, which covered the silicone cap. The cap was delicately exposed, the Arcsys system reamer was used, and a 4.2x4x2.5mm abutment was installed. A roll flap technique was performed to increase the tissue volume in the vestibular area, and a temporary crown was made over the multifunctional transfer. 60 days will be necessary for the peri-implant tissue to heal and for the final crown to be made.
Step by step
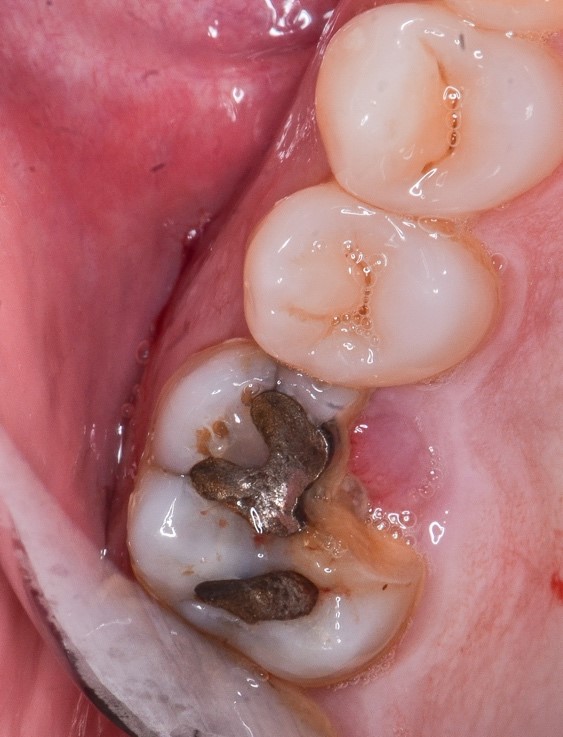
Figure 1: Element 26 dental crown with fracture compromising the biological space.
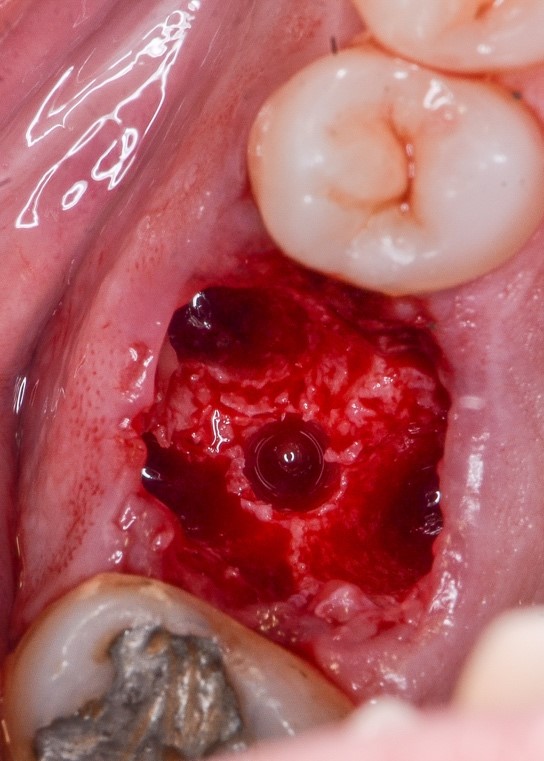
Figure 2: Interradicular septum preserved and drilled to receive the implant
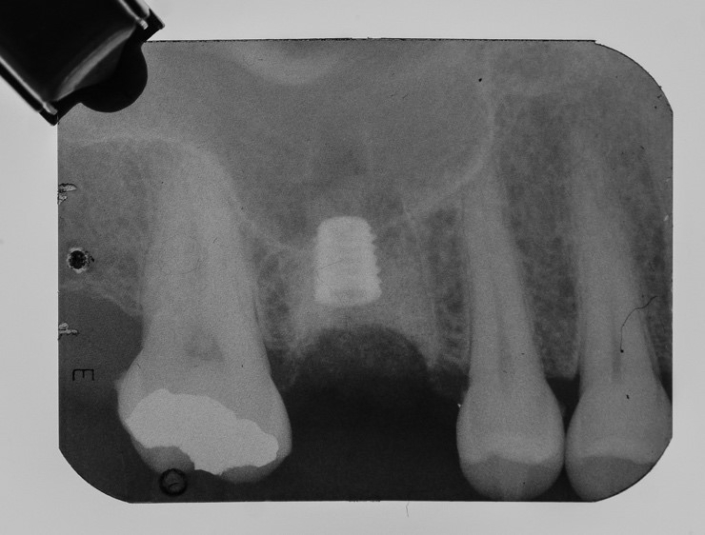
Figure 3: Arcsys 4.3x5mm implant installed in the septum and alveoli filled with Nanosynt.
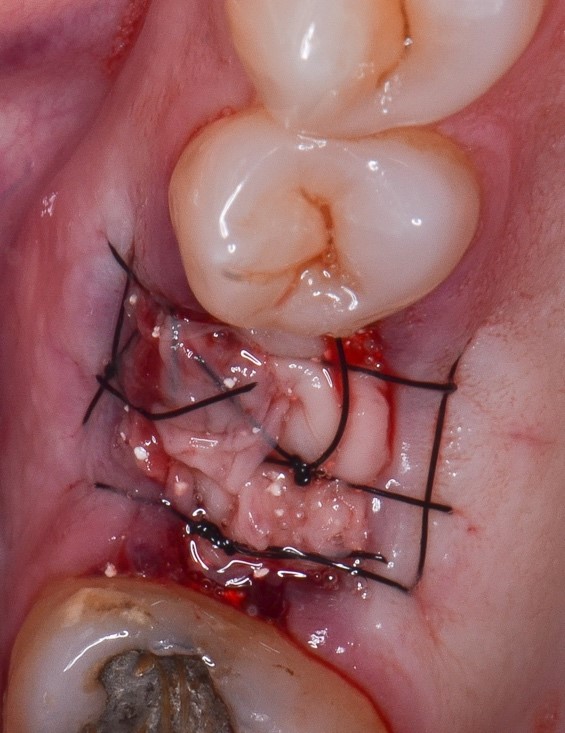
Figure 4: Socket covered with 4 membranes of leukoplate fibrin or LPRF and sutured with the open wound technique.
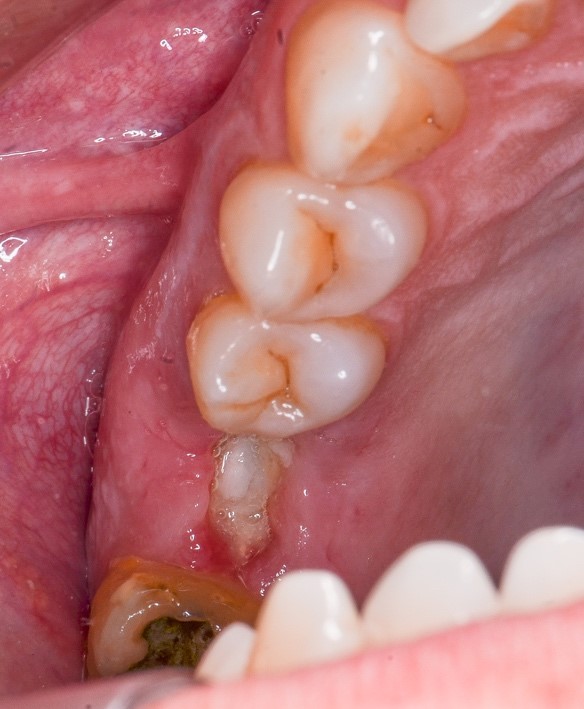
Figure 5: Clinical appearance of the wound after 7 days. Note the presence of fibrin in the room and that there is no exposure of Nanosynt
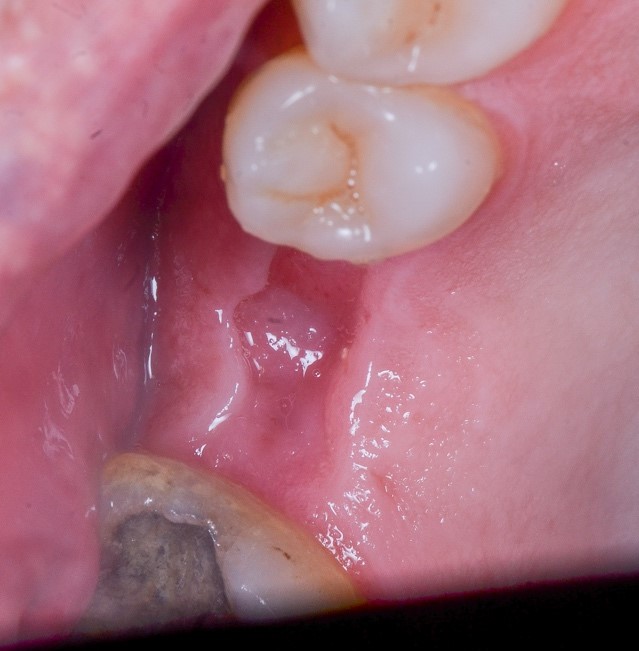
Figure 6: Clinical appearance of the area after 30 days.
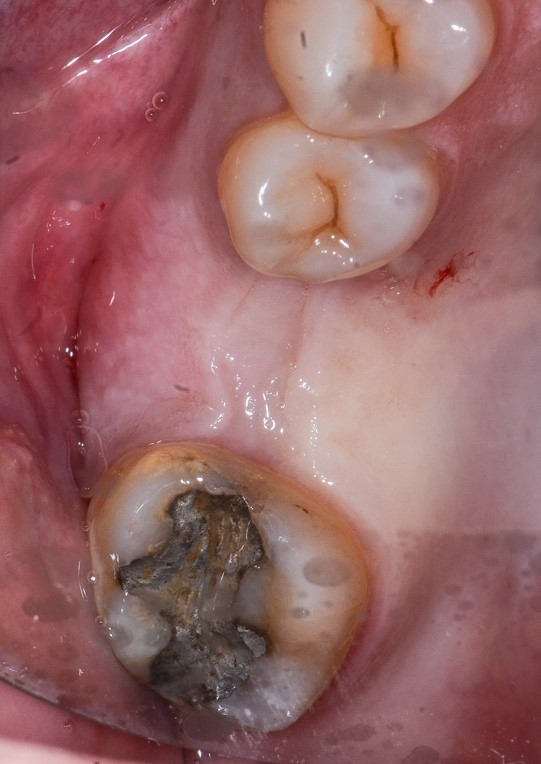
Figure 7: Appearance of the wound after 4 months. Note the formation of keratinized tissue and preservation of vestibular volume.
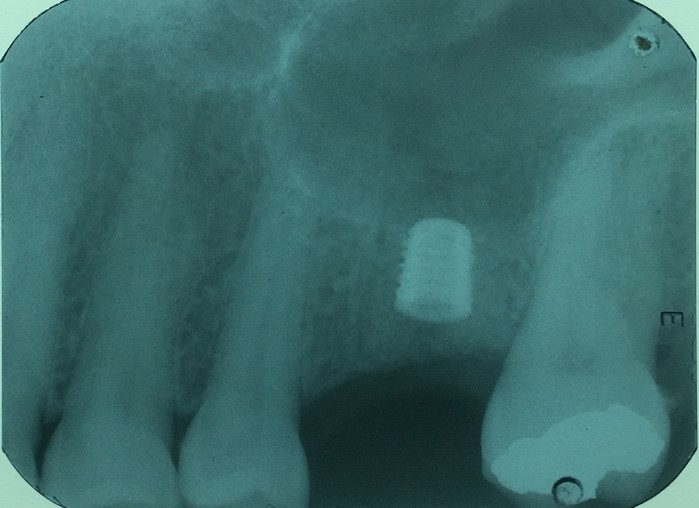
Figure 8: X-ray after 4 months of installation, to perform the reopening. Note the excellent bone formation within the bony septum.
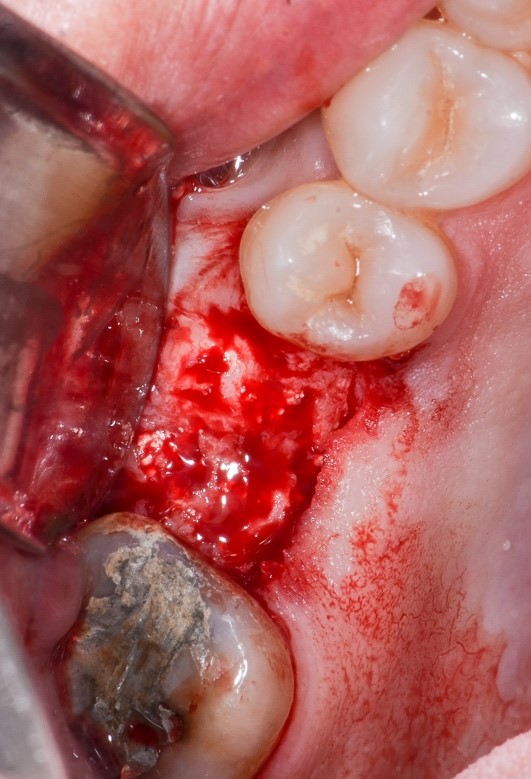
Figure 9: Clinical appearance of the area during reopening. Presence of bone formation and coating of the silicone cap.
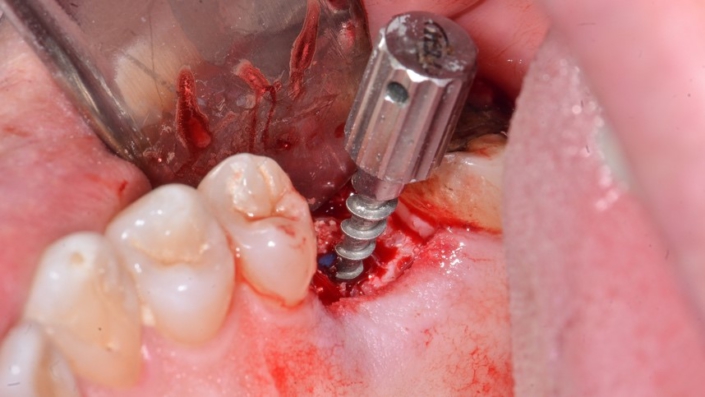
Figure 10: Removal of the silicone cap with the cap remover.
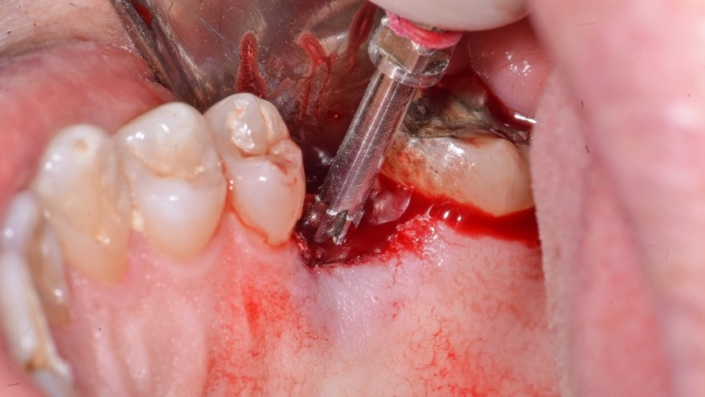
Figure 11: Use of the Arcsys reamer to remove bone tissue that prevents the seating of the prosthetic component.
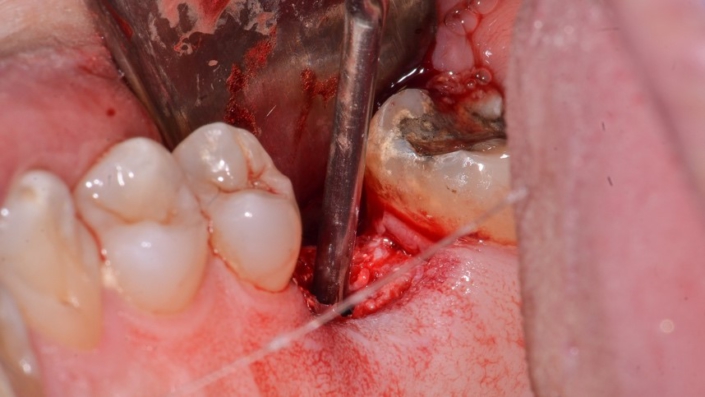
Figure 12: Aspiration of the Arcsys implant chamber using an endodontic cannula to remove debris and moisture.
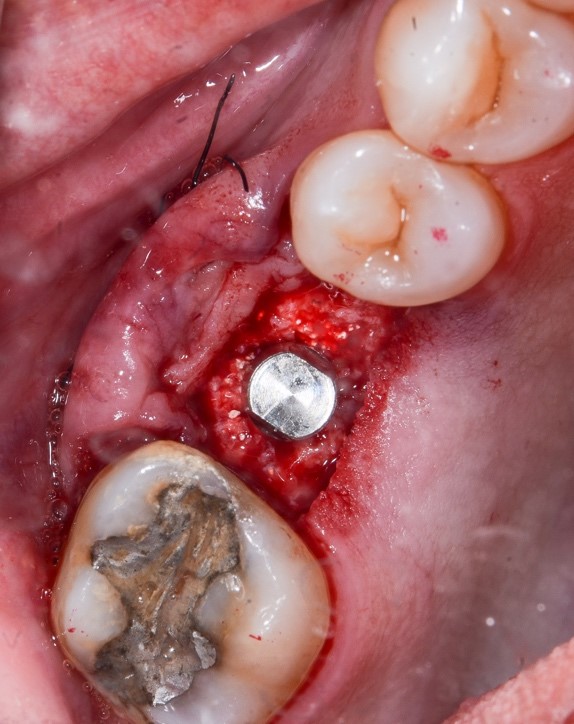
Figure 13: 4.2 × 4.2.5mm abutment installed and angled at 5 degrees. Note roll flap performed and kept in the vestibular.
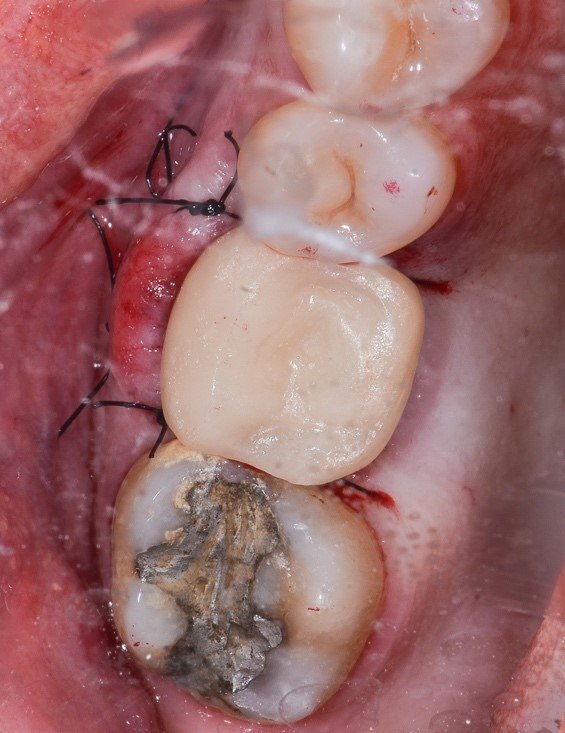
Figure 14: Temporary in acrylic composite.
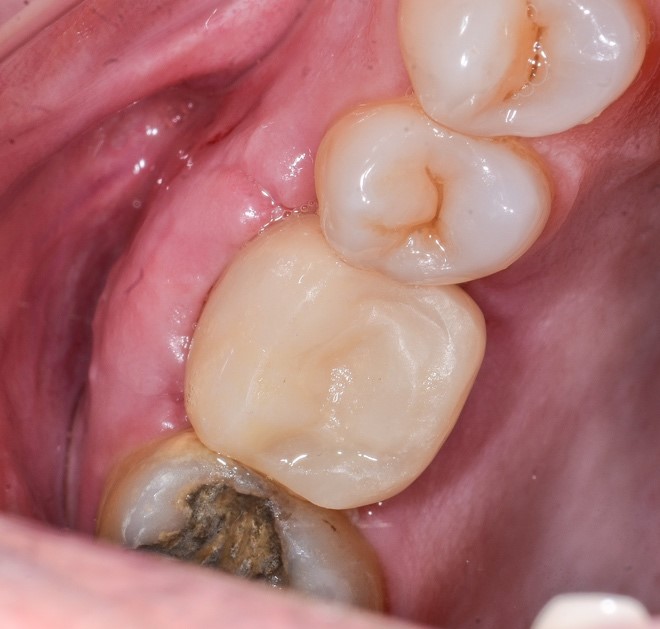
Figure 15: 7 days after the temporary installation.
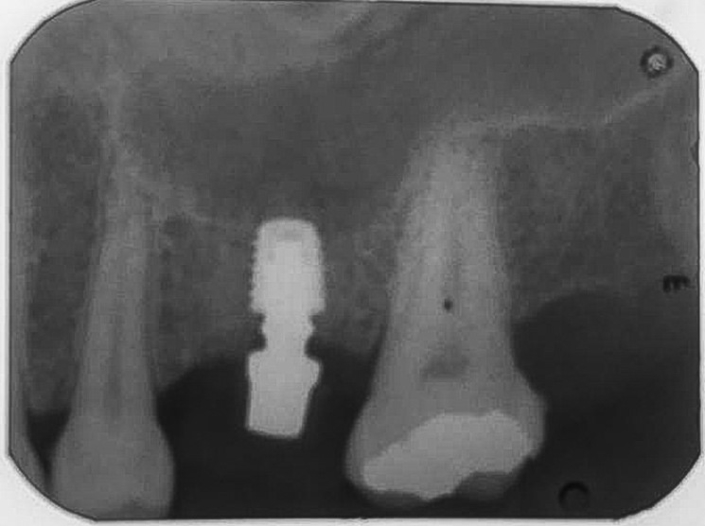
Figure 16: Radiographic appearance of the abutment installed.

![10 705x3971 1 - Arcsys short implant installed in inter-root septum and filling of alveolus with Nanosynt 10-705x397[1]](https://fgmdentalgroup.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/12/10-705x3971-1.jpg)