Authors: Dr. Thiago Roberto Gemeli, Ahylyn Restrepo Marin and Ana Karolyny Weber
14-YEAR-OLD FEMALE PATIENT
Chief complaint: Patient uncomfortable with the aspect of her smile.
Dental anomalies are deviations from normality, usually associated with the embryonic development of teeth, which may result in changes in number and shape. Agenesis is a type of anomaly associated with the absence of one or more elements, and may even be linked to some syndromes. Prevalence in global population is around 0.3%, with a predilection for females, and the inferior premolars are usually the most affected elements, followed by the superior lateral incisors.
Treatment can be shaped by professional preference, but it is usually multidisciplinary, requiring careful planning. The objective, of course, is to enable a functional, aesthetic and long-lasting rehabilitation. Therefore, orthodontic movement followed or not by prosthetic replacement of the missing element is usually the approach adopted by most professionals.
Following the philosophy of expanding the arch and replacing the missing element with a dental implant, the clinical approach described below highlights the steps taken to prepare the bone bed, prior to its installation.
CASE REPORT
A young, 14-year-old female patient sought private care because she was uncomfortable with the appearance of her smile. After anamnesis, clinical evaluation and observation of complementary exams, an orthodontic treatment was proposed to open the spaces corresponding to crowns 12 and 22. While the first was conoid, the second was absent, characterizing the presence of agenesis of this element.
The arch as a whole was expanded and element 23 was pulled and distalized. The mechanics applied required a period of 20 months to be effective and, therefore, the distal mesio space necessary for the rehabilitation of element 22 was obtained. The orthodontic appliance was removed and the patient underwent surgical intervention.
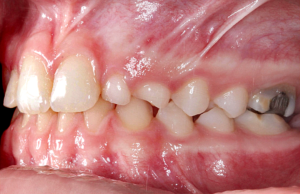
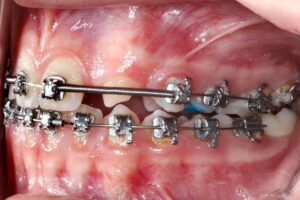
1 | Initial clinical condition. 2 | Clinical condition during orthodontic treatment.
After the incision and detachment, the cortical bone plate was pierced at several points. This approach allows the mesenchymal cells present in the trabecular stroma to migrate and differentiate into osteoblasts, colonizing the biomaterial allocated in the region.
In addition, the surgically established channels provide nutrition and optimize intercellular communication, favoring repair.
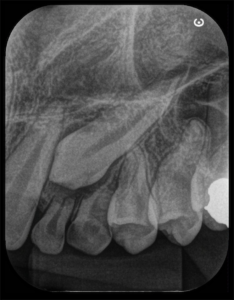
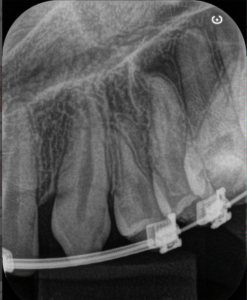
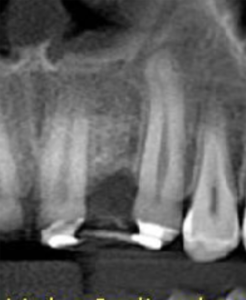
3, 4 and 5 | Imaging evolution, showing the opening of space achieved for the rehabilitation of the region corresponding to element 22.
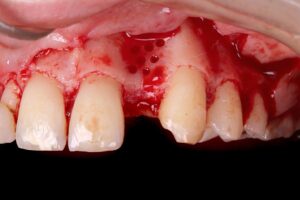
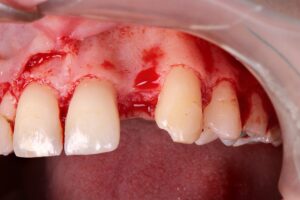
6 | Incision and detachment of tissue. 7 | Multiple perforations of the cortical bone plate.
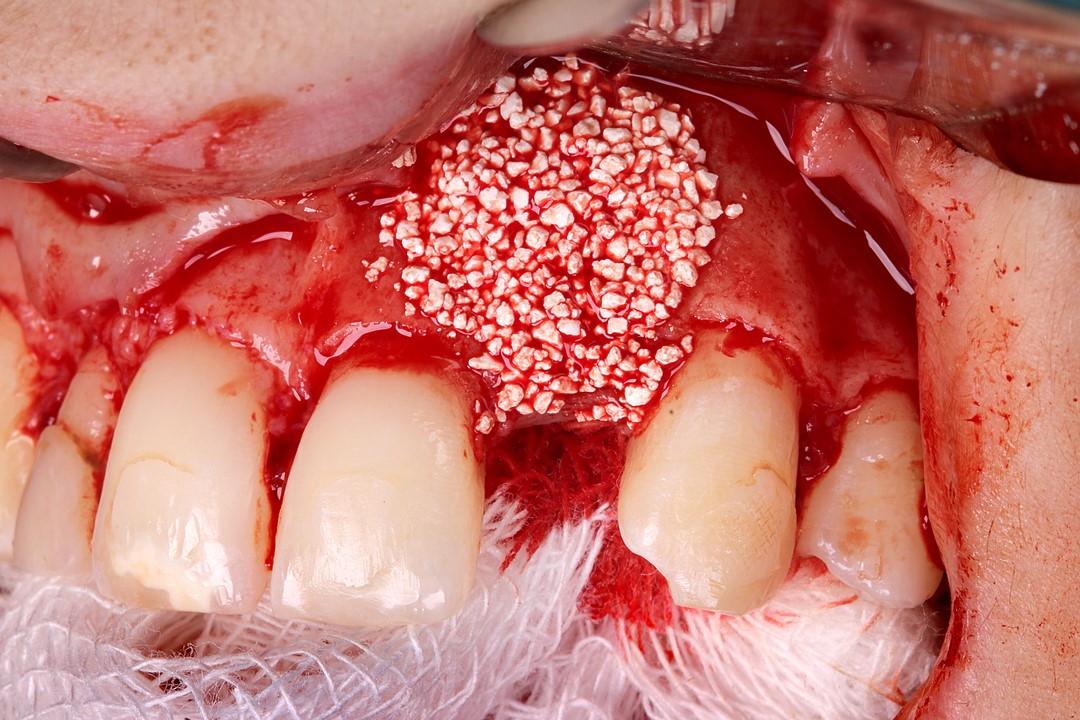
The synthetic biphasic biomaterial (granulation 500-1000 ֺm, 0.5 g) was selected because it has several desirable characteristics, such as: biological safety, substitution speed, scaffold maintenance, ultraporosity and high hydrophilicity. It should be noted that the fractionation in ampoules is also a relevant clinical advantage, due to better use of the product.
Before the stabilizing suture, the synthetic membrane, Duosynt, was used to protect and assist in targeted cell colonization, making tissue repair more predictable.
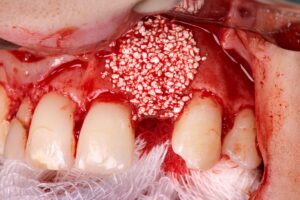
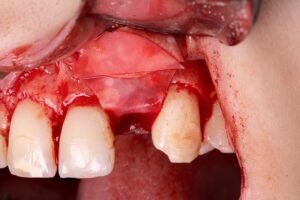
8 | Allocation of the synthetic biomaterial, Nanosynt. 9 | Accommodating the Duosynt membrane over the bone substitute.
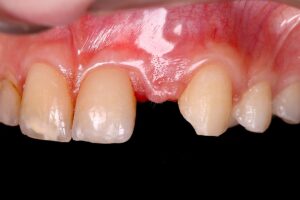
After a healing period of 21 days, a new record was made, demonstrating the adequate biological response to the imposed approaches. The provisional with bilateral palatal staples was reinstalled and the patient is currently being followed up, waiting for tissue maturation to be submitted to dental implant installation.
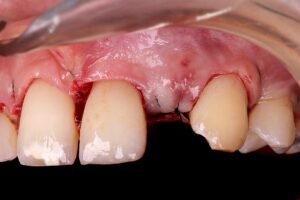
10 | Suture. 11 | Area repaired after 3 weeks.
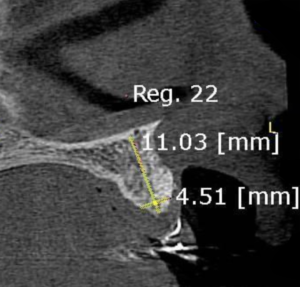
12 | Temporary adhesive in the region of element 22. 13 | Tomographic image after 21 days.

Shop FGM Implants
Shop FGM Implants
Um mundo de soluções inteligentes, em apenas alguns cliques!
- Condições especiais de parcelamento
- Promoções exclusivas
- Facilidade nos pedidos